Sriya Enterprise recently conducted an insightful Trade Finance and FEMA Workshop at SRF Limited in…

Unlock Global Opportunities: Trade Finance and FEMA Compliance Essentials for Your Business
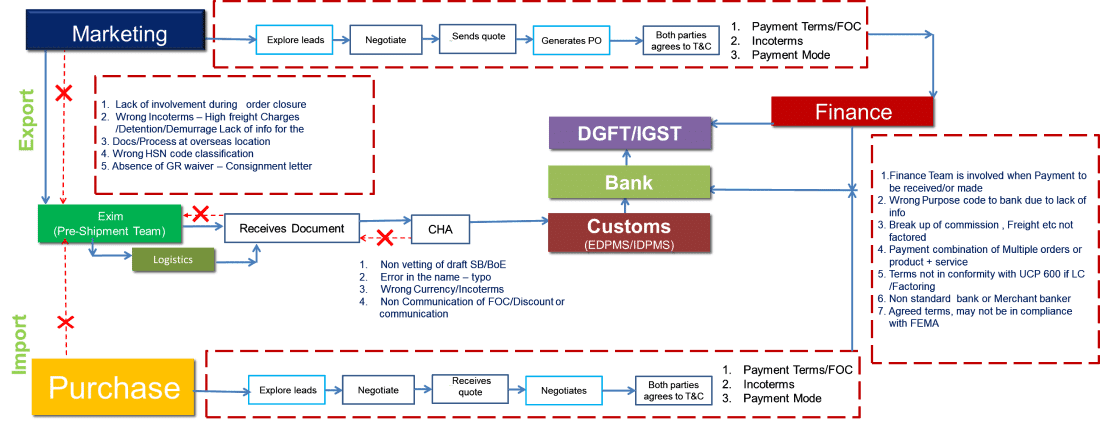
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a crucial method for identifying the underlying reasons for issues within business processes. This blog will dissect a typical RCA for Export and Import operations, highlighting common pitfalls and providing insights into how businesses can optimize their processes.
The Export Process
Marketing and Order Closure:
Steps:
- Explore leads: Identifying potential customers.
- Negotiate: Discussing terms and conditions.
- Send quote: Providing pricing information.
- Generate PO: Creation of a Purchase Order.
- Agreement on T&C: Both parties agree to the terms and conditions.
Potential Issues:
- Lack of involvement during order closure: Marketing teams may not fully engage in the finalization of orders, leading to miscommunications.
- Incorrect Incoterms: Misunderstanding international commercial terms can lead to unexpected freight charges and detention/demurrage fees.
- Inadequate information for overseas documentation and processes.
- Wrong HSN code classification: Misclassifying goods can cause customs issues.
- Absence of GR waiver/Consignment letter: Essential documentation might be missing.
Pre-Shipment (Exim Team):
Potential Issues:
- Non-vetting of draft SB/BoE: Draft shipping bills or bills of exchange might not be properly vetted.
- Errors in names (typos): Simple errors can cause significant delays.
- Wrong Currency/Incoterms: Miscommunication regarding financial details.
- Non-communication of FOC/Discounts: Failing to inform relevant parties about discounts or free-of-charge items.
The Import Process
Purchase Department:
Steps:
- Explore leads: Finding suppliers.
- Negotiate: Discussing purchase terms.
- Receive quote: Getting pricing.
- Negotiate: Finalizing terms.
- Agreement on T&C: Both parties agree to the terms and conditions.
Potential Issues:
- Non-vetting of draft SB/BoE: Lack of thorough checking of shipping documents.
- Errors in documentation: Typos and other errors.
- Incorrect currency/incoterms: Miscommunications regarding financial agreements.
- Non-communication of FOC/Discounts: Not informing all stakeholders about cost-related changes.
Key Financial Considerations
- Finance Team Involvement: Ensuring that the finance team is involved early in the process, especially when payments are to be received or made.
- Purpose Code for Banks: Correctly identifying the purpose code to avoid delays due to lack of information.
- Breakdown of Costs: Properly factoring in commission, freight, and other charges.
- Compliance with UCP 600: Ensuring terms are in line with international standards for letters of credit.
- Use of Standard Banks: Avoid non-standard banks or merchant bankers.
- Compliance with FEMA: Ensuring that all terms comply with the Foreign Exchange Management Act.
Summary
The root causes of many issues in export-import operations often stem from a lack of communication, assumptions, and a “will see” approach. By addressing these areas proactively, businesses can mitigate risks, reduce delays, and improve overall efficiency in their operations.
By identifying these potential pitfalls and implementing thorough checks and balances, businesses can streamline their export-import processes and avoid costly mistakes. Effective RCA involves continuous monitoring and updating of procedures to adapt to new challenges and ensure compliance with international standards.
If you are exploring to improve your efficiency, we at Sriya Enterprise offer our #FEMAadvisoryservices



